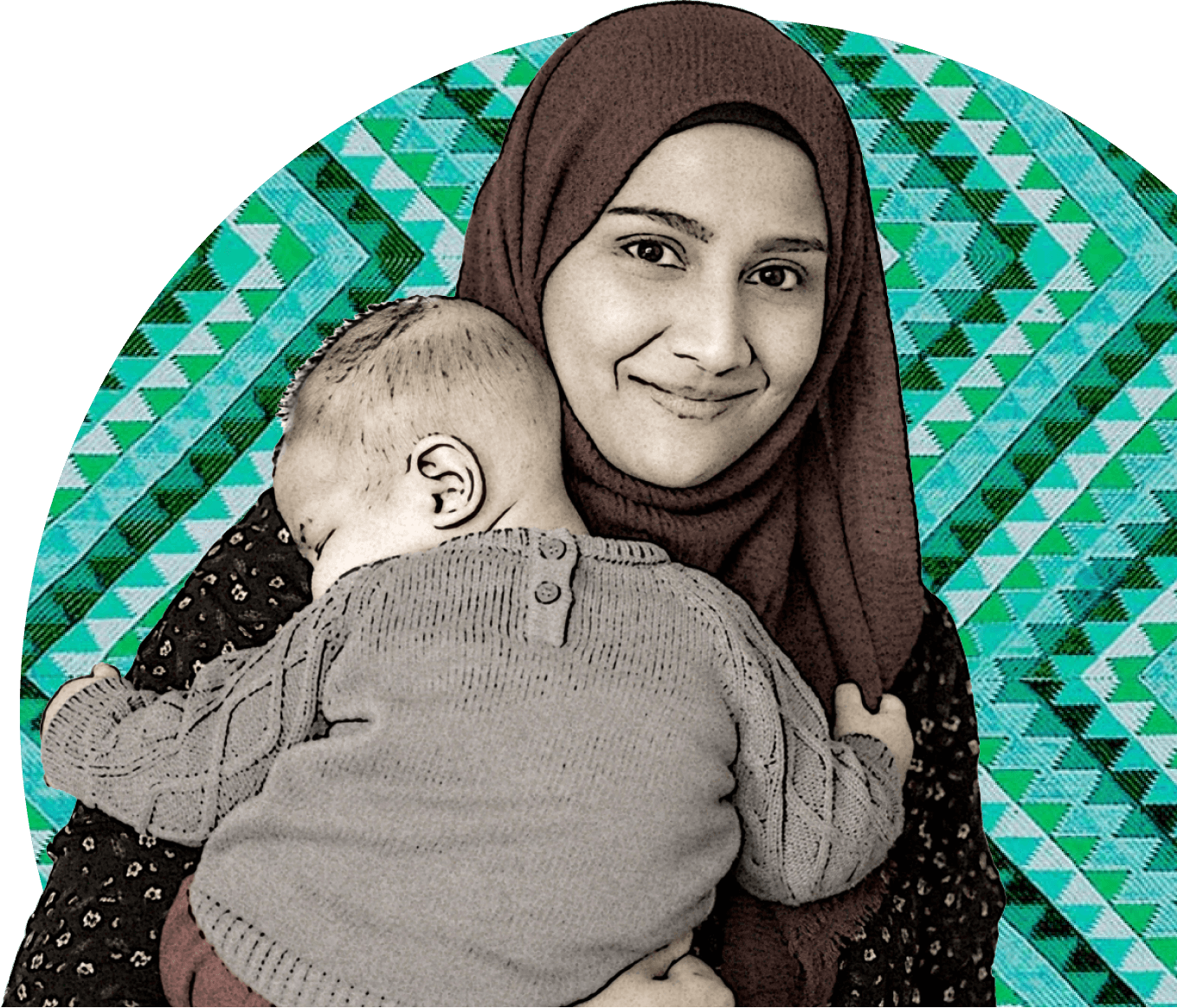
Health research for South Asians
Genes & Health is the world’s largest community-based study of genetics and health in British Bangladeshis and British Pakistanis. Our aim is to improve health in people from these communities across the UK and globally.

Help us use DNA to unlock vital clues about health and disease
Join our community of 100,000 people to contribute to improve the health of future generations of British Pakistani and British Bangladeshi people.
British Bangladeshi and British Pakistani people have some of the highest rates of heart disease, diabetes, and poor health in the UK. Genes & Health is finding better ways to prevent, diagnose and treat these conditions, and many others, using genetic and health information.
Our volunteers are making a vital contribution that will improve the health of future generations. It is quick and simple to become a volunteer.
Our research teams are leading valuable research across the NHS, community settings, places of worship and in academic and life sciences organisations. You can find out more about our research here:
Joining Genes & Health is easy! Watch our video below in your preferred language to find out how
Our volunteers so far
70,014